Cannabinoids (KA-nuh-bi-noydz) are a group of compounds present in cannabis. The broader definition of cannabinoids refers to a group of substances that are structurally related to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or that bind to cannabinoid receptors.
Natural Cannabinoids[]
THC[]
THC is the most commonly referenced cannabinoid, and is responsible for much of the psychedelic quality in cannabis. It is the active compound in the prescription Marinol.
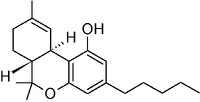
Structure of THC
CBD[]
Cannabidiol (CBD) is not psychoactive on it's own, but does effect psychoactivity of THC. However, recent evidence shows that smokers of cannabis with a higher CBD/THC ratio were less likely to experience schizophrenia-like symptoms. This is supported by psychological tests, in which participants experience less intense psychotic effects when THC was combined with CBD.Medically, it appears to relieve convulsion, inflammation, anxiety, and nausea. CBD has a greater affinity for the CB2 receptor than for the CB1 receptor.[8] It is perceived to have more effect on the body. CBD shares a precursor with THC and is the main cannabinoid in low-THC Cannabis strains.
CBD also delays the onset of the high but can make it last considerably longer (as much as twice as long). The kind of grass that takes a while to come on but keeps coming on.
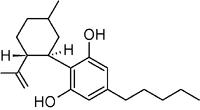
Structure of CBD
CBN[]
CBN (Cannabinol) is produced as THC ages and breaks down, this process is known as oxidization. High levels of CBN tend to make the user feel tired and stoned rather than high. CBN levels can be kept to a minimum by storing cannabis products in a dark, cool, airtight environment. Cannabis should be dry prior to storage, and may have to be dried again after being stored somewhere that is humid.
This is partly why stale cannabis does not produce the same high as fresher cannabis.

Structure of CBN
THCV[]
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is prevalent in certain South African and Southeast Asian strains of Cannabis. It is an antagonist of THC at CB1 receptors and attenuates the psychoactive effects of THC.
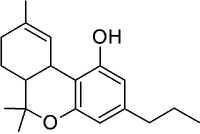
Structure of THCV